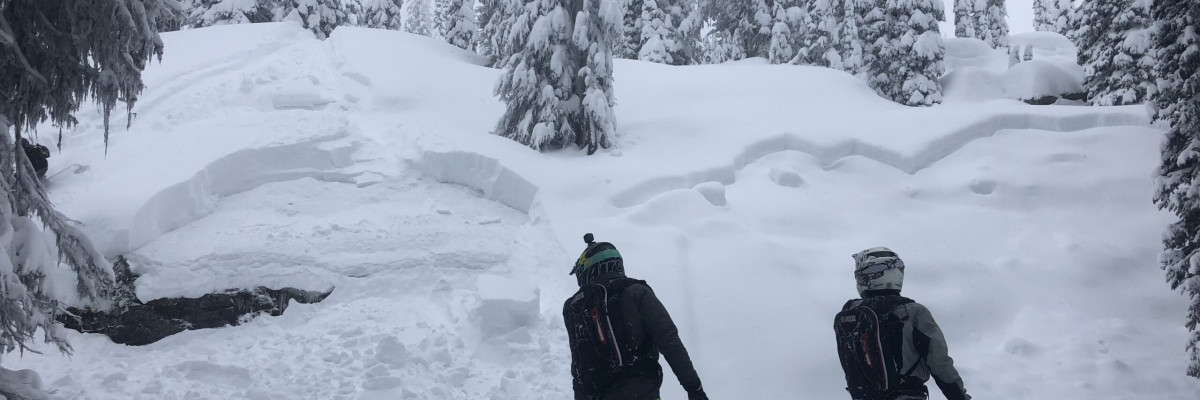
Good morning, this is Travis Craft with the West Central Montana Avalanche Center’s weather and avalanche update for December 27, 2017. This danger rating does not apply to operating ski areas, expires at midnight tonight and is the sole responsibility of the U.S. Forest Service.
Weather and Snowpack
Mountain temperatures range from 11 F to 23 F in the region. Winds are 7 mph with gusts of 13 mph out of the SW in the Bitterroot. Point Six, in the northern part of the advisory area, winds are 20 mph with gusts of 28 mph out of the W. The advisory area received 2 to 4 inches of snow in the last 24 hours.
Primary avalanche problem is wind slabs. Look for rounded pillows of snow near ridgelines and recognize signs of instability such as cracking in the surface snow. Look for cross-loaded terrain as well as ridge tops.
The second avalanche problem is persistent slabs. Dig a pit to assess how reactive these layers are before committing to any slope over 30 degrees.