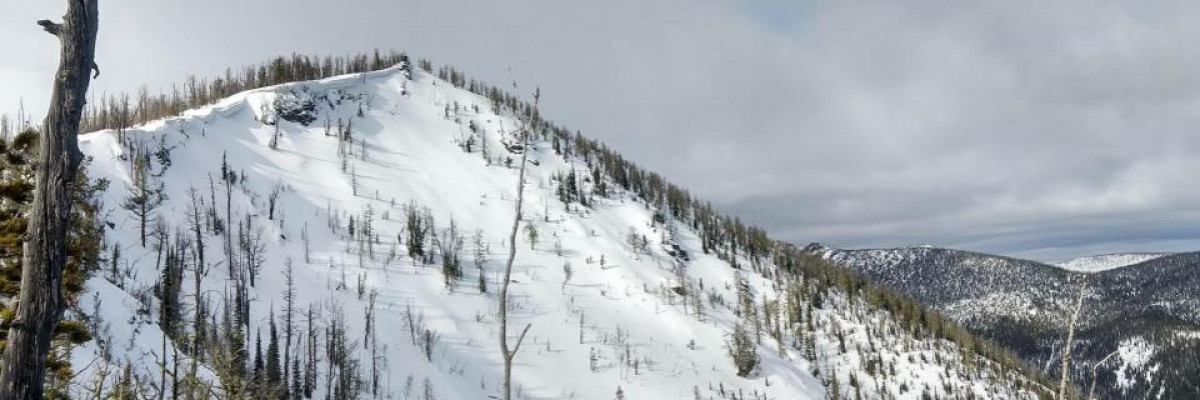
The avalanche danger is moderate in the Rattlesnake and low in the central and southern Bitterroot, and Seeley Lake zone. It is possible to trigger an avalanche in the Rattlesnake. There are isolated avalanche problems in the other zones. Low does not mean no avalanche danger.
Good Morning. This is Travis Craft with the West Central Montana Avalanche Center advisory on Saturday, January 23rd, 2021. This advisory is sponsored by LB Snow. This advisory does not apply to operating ski areas and expires at midnight tonight. The USDA Forest Service is solely responsible for its content.
Weather and Snowpack
Mountain temperatures range from 13 degrees to 22 degrees F this morning. No new snow overnight.
The snowpack is gaining strength throughout most of the region. Shallow snowpacks( 3 feet deep) are the weakest. You can find these shallow points in lower elevations and throughout the Rattlesnake. Yesterday, we saw small point releases in Lolo, St Mary’s, Seeley Lake area, and the Rattlesnake. The Jan 13 rain crust is the layer to investigate before committing to avalanche terrain. There are facets below the crust that are sometimes reactive in pit tests. The Rattlesnake has the weakest, shallowest snowpack. The weak structure in the Rattlesnake is creating Moderate avalanche danger.
Today, I would choose simple, low angle slopes and avoid slopes with shallow snowpacks in the Rattlesnake. In the rest of the advisory area, I would avoid wind-loaded terrain, choose simple slopes, and then work into more complicated terrain. The places to avoid on slopes are near cliff bands, rocks, and rollovers. These areas will have shallower snowpacks where it more likely to trigger an avalanche.
Bottom Line
Today, do your homework before committing to steep slopes. Avoid slopes with weak sugary snow. Do multiple pits investigating the stripes in your pit wall. Avoid cornices and wind loaded terrain. Choose simple terrain that does not expose you to terrain traps. Avoid likely trigger points on slopes.
Travel one at a time in avalanche terrain, carry a beacon, shovel, and probe. Remember to reassess conditions throughout the day and stay alert for signs of instability. Dig a pit. Look for red flags.
Upcoming Education Events:
Please visit our education page for an up to date list of regional educational events and course offerings. Below are a few select events and opportunities to check out.
- January 26th-31st | Motorized AIARE 1 Course | Delivered by the Mountain Riding Lab | Get more details and register HERE
- January 27th, 6-7:30 PM MST | FREE Online 1.5-hr Avalanche Awareness Session | Missoulaavalanche.org event | Delivered by A3 Pro instructors | Get more details and register HERE
- February 6th | Motorized Avalanche Rescue Course | Delivered by the Mountain Riding Lab | Get more details and register HERE
- February 7th | Motorized Avalanche Rescue Course | Delivered by the Mountain Riding Lab | Get more details and register HERE
Public Observations
Thank you to everyone who has taken the time to send in a public observation. Please keep sharing what you find and see while out in the backcountry. This online forum is a great resource to glean information about current conditions.
Remember, you can submit your observations through the observation page anonymously. When submitted anonymously, the forecasters review the observation and utilize it when generating the forecast. The information does not appear on the public observation page.
Ski and ride safe.